Before diving into Virtual Private Cloud concepts useful for the exam, let’s start with the main concepts/components of AWS Global Infrastructure, in regards with closeness to the end user, and where our resources resides - on-premises or in the cloud.
AWS Global Infrastructure
- Region: collection of AZ geographically closely located (usually same city) so that worldwide customer base can take advantage of low latency connections; regions also allow compliance with with regulations, laws and governance relating data storage. (currently 26+)
- Availability Zone : essentially physical data centers; 2 or more in each region, isolated from each other using separate power and network connectivity.
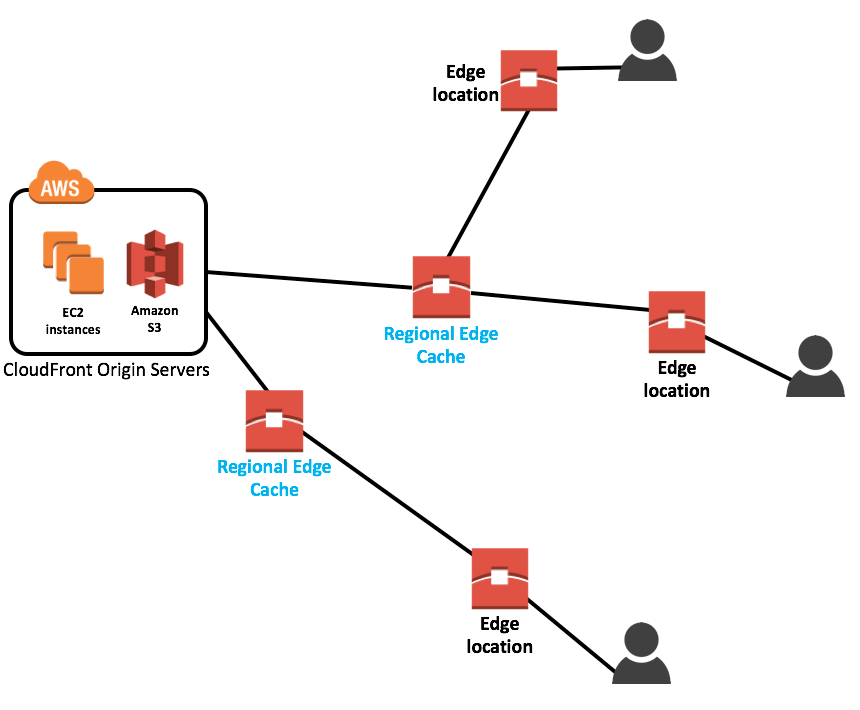
- CloudFront: is a CDN, to get content closer to users
- Edge location: AWS sites deployed in major cities/ highly populated areas. Not used for deployment our own infrastructure, but used by many services like CloudFront and Lambda@Edge to cache and reduce latency.
- Regional Edge Cache: AWS sites located between Cloudfront Origin servers and Edge Location; they have a larger cache than individual Edge location and lower latency than Cloudfront.
- AWS Outposts: with outpost you can run some AWS services on dedicated hardware within your on-prem data centers
- AWS Local Zones: for ultra low latency applications (live video, MRL, AR/VR)
- AWS Wavelength Zones: similar to LocalZone but for 5G devices (single digit ms latency)
- VPC (Virtual Private Cloud): a logically isolated portion of AWS cloud within a region
- Private and Public subnets: a range of IP addresses in the VPC where we can place groups of isolated resources
Also some introductory concepts as IP Addressing, CIDR Blocks and Subnetting is necessary to understand how to properly configure a VPC:
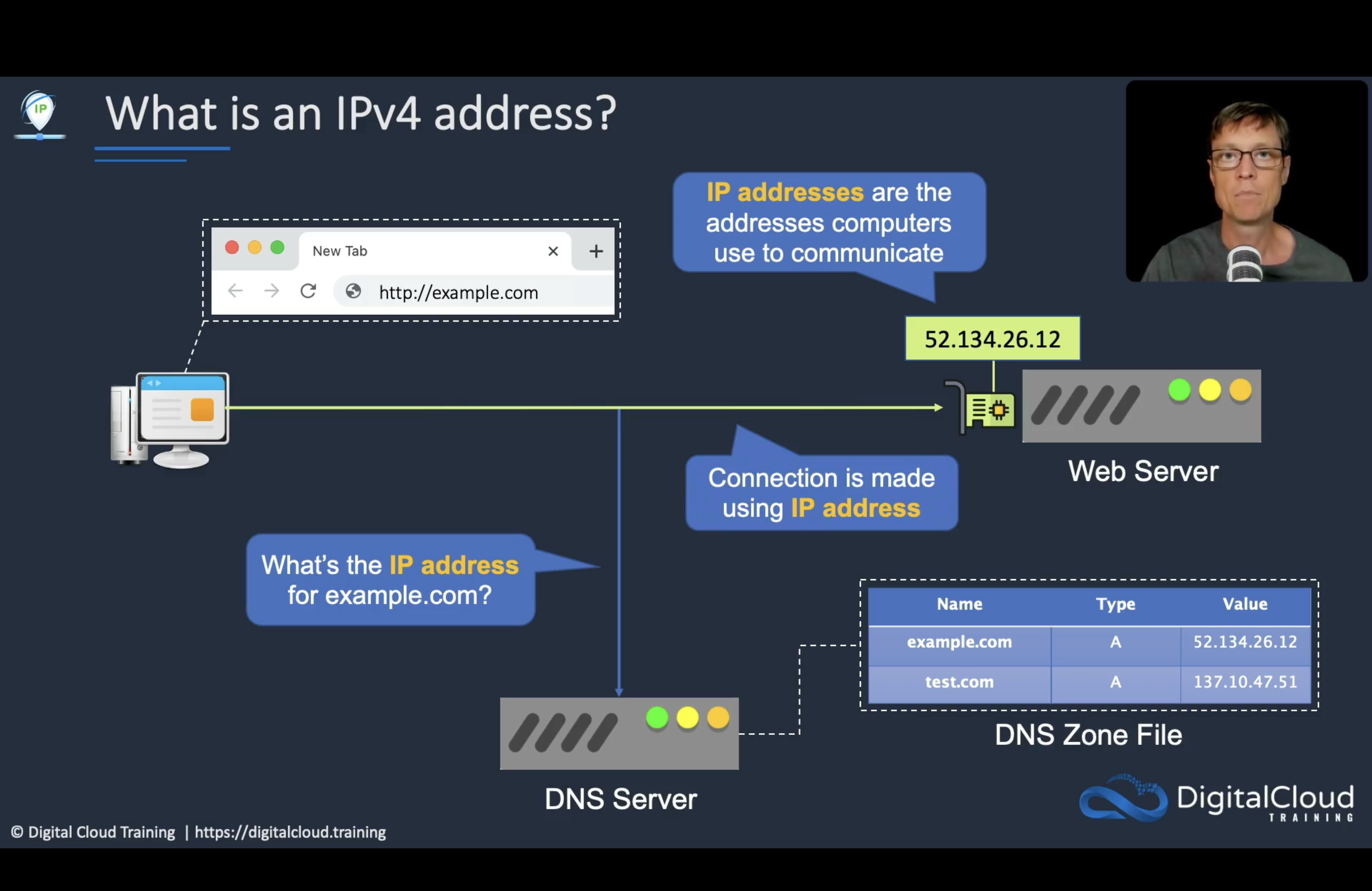
##IPv4 and IPv6 Addressing
An IPv4 address is 32 bits long (4 octets ): this means there are 4.3 billion addresses available which are going to be soon exhausted.
The first 3 binary octects are Network Id, while the last one is the Host ID Different Computers on same Network will have same NetworkId, ( like 192.168.0) but have unique HostIDs.
IPv6 addresses are 128 bits long and use hexadecimal instead of dotted decimal.
When using IPv6 for VPC CIDR Block AWS will provide a /56 CIDR block from their own pool.
All IPv6 addresses are publicly routable and no NAT is necessary. If we want to allow only outbound traffic, we can use egress-only internet gateway.